What’s a good credit score? Let’s unpack it.
Building strong credit starts with understanding it. Credit Karma is here to make the process easier with tips, tools and insights.
 Image: what is a good credit score
Image: what is a good credit scoreEverything you need to take your credit to the next level.
 Image: test
Image: testCredit building
Get credit-boosting tips and insights. Plus, see how you could improve a low score with Credit Builder1 from Credit Karma Money™.
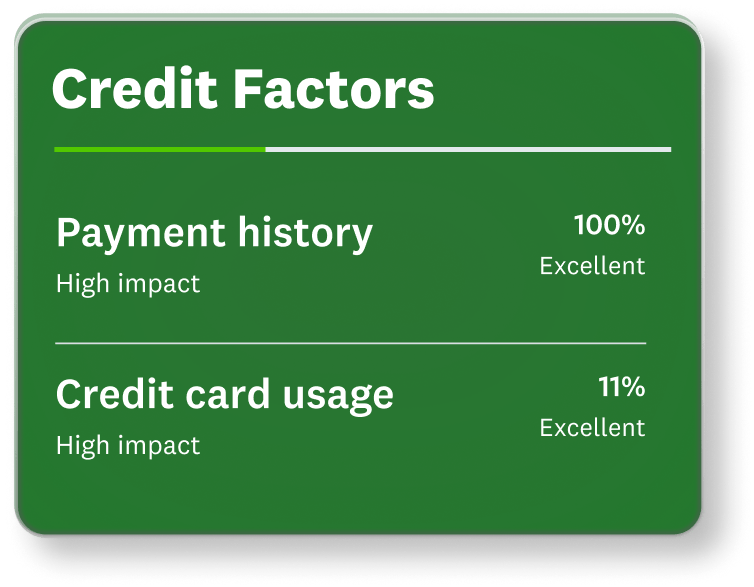 Image: New_CreditFactors
Image: New_CreditFactorsFactor breakdowns
See the key factors that make up your credit scores so you know exactly what to focus on to improve your credit.
 Image: New_FindaCard
Image: New_FindaCardSmart offers
Choose from credit card and loan options that could work best for you and help you reach your goals.
Editorial Note: Intuit Credit Karma receives compensation from third-party advertisers, but that doesn’t affect our editors’ opinions. Our third-party advertisers don’t review, approve or endorse our editorial content. Information about financial products not offered on Credit Karma is collected independently. Our content is accurate to the best of our knowledge when posted.
What is a good credit score?
Updated October 17, 2025
This date may not reflect recent changes in individual terms.
Written by: Brad Hanson
Key takeaway: There is no such thing as a single “good” score — multiple credit scoring models and providers all define their scores differently — but generally scores between the high 600s and mid-700s would be considered within a “good” range.
There’s no one definition of a good credit score. That’s because there are many different credit scores that depend on unique scoring models. And keep in mind that different lenders have their own standards for rating credit scores.
As a general rule, scores starting in the high 600s and up to the mid-700s (on a scale of 300 to 850) are considered to be “good.”
Each credit-scoring model uses a unique formula to calculate credit scores based on the information in your credit reports.
Even well-known credit-scoring systems FICO and VantageScore have multiple credit-scoring models or versions that produce different scores. (Credit Karma offers free VantageScore 3.0 credit scores from Equifax and TransUnion.)
- How a good credit score can help you
- What factors affect my credit scores?
- Credit score ranges
- Credit scores needed for your financial goals
- Where can I check my credit score for free?
- Credit score FAQs
VantageScore 3.0
The VantageScore® credit scoring model was created in 2006 through a partnership between the three major credit bureaus: Experian, TransUnion and Equifax. With a score range of 300 to 850, VantageScore 3.0 offers increased access to scores for those with limited credit history.
VantageScore 3.0 score ranges
- Poor: 300–600
- Fair: 601–660
- Good: 661–780
- Excellent: 781–850
FICO score
Fair Isaac Corporation, or FICO, has created a variety of credit-scoring models that lenders, credit card issuers and other creditors use to gauge a borrower’s potential credit risk. FICO’s different credit scoring models generally consider ranges from 670 to 739 as “good.”
FICO® 8 and 9 consumer score ranges
- Poor: 300–579
- Fair: 580–669
- Good: 670–739
- Very good: 740–799
- Exceptional: 800–855
How a good credit score can help you
A credit score is a numeric representation, based on the information in your credit reports, of how “risky” you are as a borrower. In other words, it tells lenders how likely you are to pay back the amount you take on as debt.
Credit scores are one piece of the puzzle that lenders look at to determine whether to lend to you. A good credit score can help you get access to a greater variety of loan offers.
And if a lender approves your application for credit, a good or excellent credit score can help you qualify for lower interest rates and better terms.
In general, the higher your scores, the better your chances of getting approved for loans with more-favorable terms, including lower interest rates and fees. And this can mean significant savings over the life of the loan.
Having a good score doesn’t necessarily mean you’ll be approved for credit or get the lowest interest rates though, as lenders consider other factors, too. But understanding your credit scores can help you decide which offers to apply for — or how to work on your credit before applying.
What factors affect my credit scores?
Many factors can affect your credit scores. Here are some of the main ones:
Your payment history is a record showing how consistently you’ve paid your credit accounts over time, including on-time payments and late payments.
Keeping your credit card balances low can not only save you money on interest, but can also help keep your credit utilization rate down. A good rule of thumb is to keep credit utilization below 30% of your total credit limit.
A longer credit history can help increase your credit scores by showing that you understand credit and have been using it for a long time. Keeping your oldest accounts open can ensure that your overall credit history continues to age.
Your credit mix reflects the different types of credit you have on your reports, from credit cards to student loans. We don’t recommend applying for a loan just to get another type of credit account on your reports, but it’s good to know that this can factor into your scores.
A hard inquiry can occur when a credit card issuer checks your credit before deciding whether to approve your application. Too many hard inquiries in a short period of time may be a sign of a high-risk borrower who’s opening a lot of accounts because of a financial pinch.
Learn more about the factors that affect your credit scores.
Credit score ranges
While there are many different credit scores, the most common models use a scale ranging from 300 to 850. Within this scale, there are some general credit score ranges that can help you interpret what your scores mean.
Here are the credit score ranges to be aware of and what they mean for you.
 Image: Poor
Image: PoorPoor credit scores: 300 to low-600s
Poor credit can make it harder to get loans or unsecured credit cards, but you still may have options. Secured credit cards, for example, can help you build or rebuild your credit. But be aware of potential fees and higher interest rates. And make sure the lender reports to the three major consumer credit bureaus — Equifax, Experian and TransUnion — so that your on-time payments can help improve your scores.
 Image: Fair
Image: FairFair to good credit scores: Low-600s to mid-700s
If your credit score is in this range, you have a better chance of being approved for financial products and can shop around to compare options from different lenders. But you might not qualify for the most favorable terms.
 Image: VeryGood
Image: VeryGoodVery good and excellent credit scores: Above mid-700s
While lenders look at a variety of factors when considering a credit card or loan application, people with top credit scores are the most likely to be approved for loans and credit cards with low interest rates and good repayment terms.
What is the highest credit score you can get?
For the major consumer credit scores, generally the highest credit score you can get is 850.
Keep in mind that perfect credit scores aren’t usually necessary to qualify for competitive rates on loans and mortgages.
Once you’re in the “very good to excellent” range, you likely won’t see much of a difference in terms of interest rate offers from, say, a 790 to an 840. Moving from a 650 to a 700 will likely have a more significant impact, which is why the general credit score ranges are important benchmarks to consider.
Credit scores needed for your financial goals
 Image: good credit score
Image: good credit scoreWhat’s a good credit score to buy a house?
The average credit score for first-time homebuyers in the U.S. was 758, a recent Experian analysis found, which falls in the “very good” credit range.
In general, aiming for a score in at least the high 600s to mid-700s can help you qualify for many mortgage loans and improve your chances of getting more-favorable rates and terms.
Credit requirements for home loans vary by loan type and lender. For instance, government-backed options such as FHA loans often have lower minimum credit score requirements than conventional loans, and individual lenders also maintain their own specific guidelines.
What’s a good credit score to rent an apartment?
Prospective landlords may run a credit check before you can sign a lease, but there’s no single credit score benchmark you need to hit to be able to rent an apartment. It can depend on the factors the landlord is looking for in a tenant, as well as where you’re looking to rent.
What credit score do you need to get a credit card?
It’s possible to get approved for a credit card with poor credit — or even no credit at all. If you have no credit, look for secured cards or cards for beginners (like student cards).
If you have limited or poor credit, secured cards or cards advertised for building or rebuilding credit could be a helpful leg up. Once you’ve improved your credit, you may be able to qualify for more-enticing offers, such as rewards cards or balance transfer cards.
What credit score is needed to buy a car?
You may be able to get approved for a car loan with a poor credit score, but it could be more difficult to find one to qualify for, and you could face high interest rates.
The average VantageScore 4.0 credit score for new car buyers was 755, according to Experian’s State of the Automotive Finance Market report for the fourth quarter of 2024.
If you’re still working on your credit and can’t wait to take out a car loan, consider asking a trusted family member or friend to act as a co-signer, or see if you can put down a larger down payment.
Where can I check my credit score for free?
Credit Karma, though not a bureau itself, provides free VantageScore 3.0 scores and reports from two of the three main credit bureaus, Equifax and TransUnion. By regularly monitoring your credit, you’ll be able to track changes and learn more about the factors currently determining your credit scores. You may also be able to view your credit scores from your existing bank or credit card lender if you have an existing membership.
Credit score FAQs
It depends on where you’re starting from and what challenges you’re facing. But building good credit probably won’t happen overnight. The important thing is to work steadily toward getting your credit in good shape and understand that building credit is a journey.
If you’re brand new to credit, it could take months of using beginner products like secured cards or a credit-builder loan to make significant progress in the types of financial products you qualify for. If you have issues on your credit reports, like late or missed payments or a bankruptcy, it could take years for those derogatory marks to fall off and stop affecting your scores.
You can get your VantageScore 3.0 credit scores from Equifax and TransUnion for free on Credit Karma. Checking your own scores won’t hurt your credit.
Since your credit history changes over time, regular monitoring is important for staying on top of your credit health. This can help you spot errors and understand the factors that affect your scores. With Credit Karma’s free credit monitoring, you’ll receive alerts and tips to help improve your credit.
Although age is not a direct factor in calculating credit scores, average credit scores generally tend to increase with age.
Younger adults generally have lower scores compared to older generations, based on average VantageScore 3.0 scores for Credit Karma members with debt in 2025.
- Gen Z: 657
- Millennials: 668
- Gen X: 674
- Baby Boomers: 716
- Silent Generation: 737


